
by David Hubbell | Aug 10, 2020 | Mirliton
Background:
On June 20th, 2020, Mirliton.org announced the we were kicking off the Ishreal Thibodeaux White Mirliton Preservation Project in an attempt to bring back, from the brink of extinction, this rare ivory white variety of the mirliton grown and cared for over four decades by Opelousas, Louisiana’s Ishreal Thibodeaux. Since that time, the Phase 1 growers have been continuing toward our goal of both growing and educating the public on this variety as well as the project in general. Originally this venture had four official growers agreeing to adhere to the strict guidelines that were put forth in the preservation plan. ( https://www.mirliton.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/Ishreal_Thibodeaux_White_Mirliton_Preservation_Project.pdf)
They are: Keith Mearns with the group Historic Columbia in Columbia, South Carolina; Chris Smith with The Utopian Seed Project in Asheville, North Carolina; Paul D’Anna a long-time independent grower in Metairie, Louisiana; and Chef John Folse growing these at his White Oak Estate and Gardens in Baton Rouge, Louisiana. In addition to these, two other long-time independent growers were added to the official group: James Cobb in Houma, Louisiana and myself, David J. Hubbell in Mobile, Alabama. In addition to the official group, a few pots of sprouted Ishreal Thibodeaux mirlitons were made available to some experienced mirliton growers with the hopes they will also report in on their independent progress.
One thing that may not have been clearly stated is what we will consider success for the Ishreal Thibodeaux White Mirliton Preservation Project? One goal is to re-establish 20-30 sustainable vines that can endure for 5 or more years with long term committed growers willing to dedicate the “rest of their life” to caring for the vines or being the “keeper of the flame”. They would be connected via a network to be able to resupply each other should one lose their crops, plus we could have some guidelines that they maintain to improve their chances going into the future as well as finding someone else to take over for them at some point. Lance Hill has also suggested: “I think a goal of an initial five growers and each year after then, double that number (each grower recruits another grower.) “This plan will surely put us on a path to get to 20-30 growers in just a few years. The key to this will be to also adequately educate the new growers to hopefully plan for issues in the future.
Distribution:
The seed mirliton for the project were provided by Paul D’Anna and Chef John Folse. On June 29th, Chef John carefully packaged four sprouted seed mirliton to send to our growers. These mirliton were wrapped loosely in bubble wrap and placed two to a box, then shipped second day UPS to our Carolina growers.
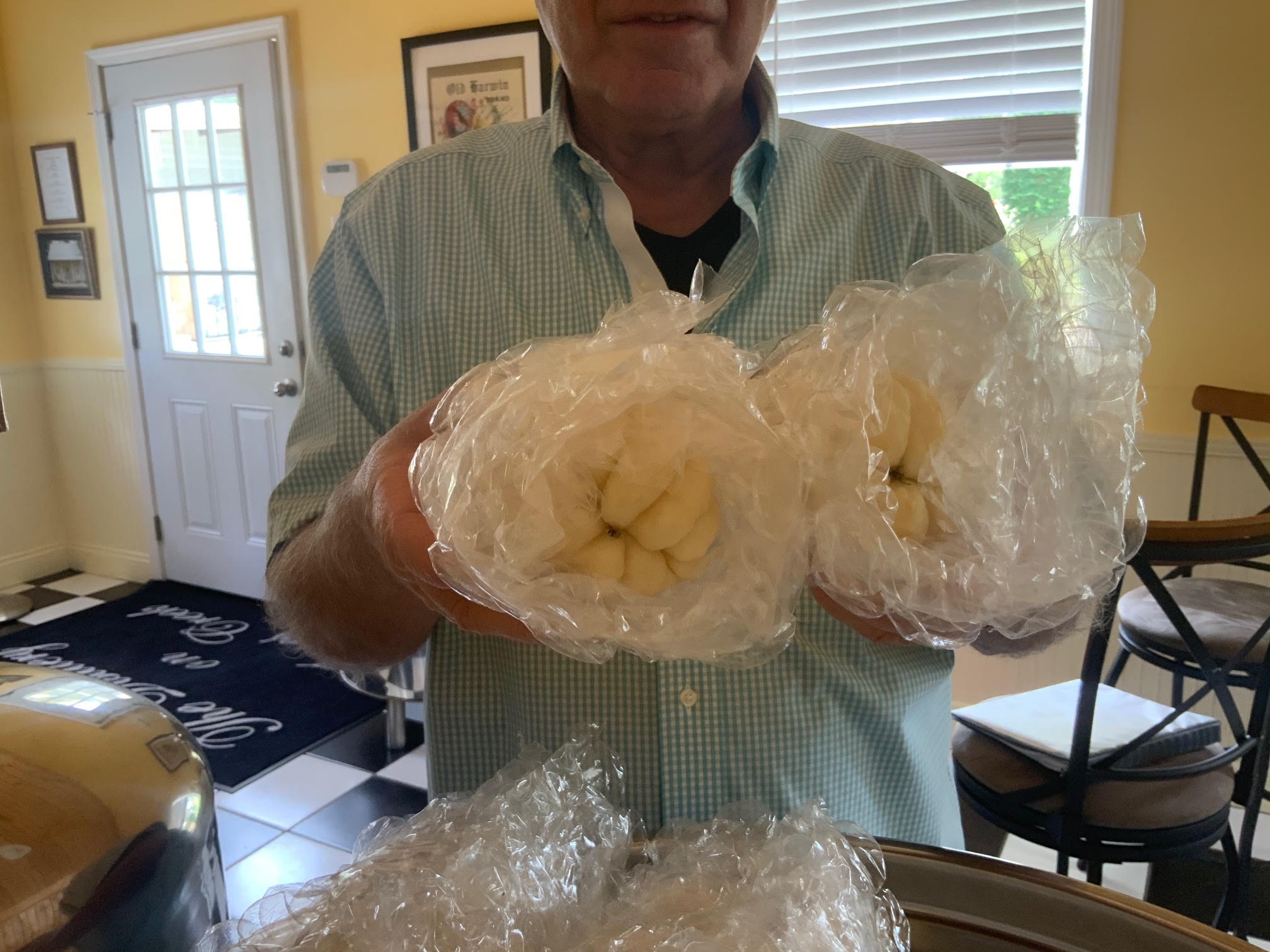

Image 1. Chef John Folse showing the meticulously wrapped mirliton for shipping.
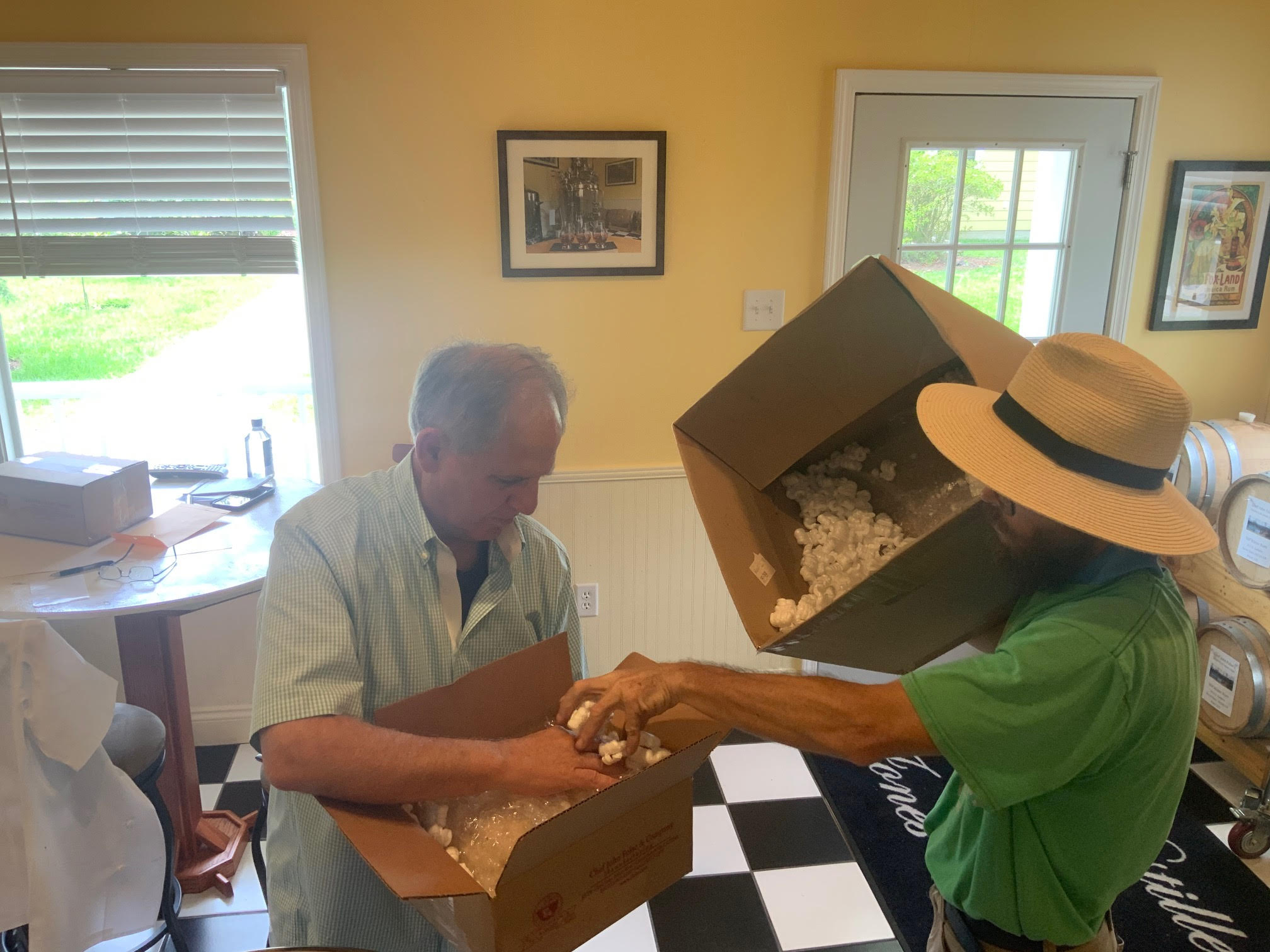

Image 2. Chef John Folse and White Oak Gardener Brian Ainsworth finishing the packaging the seed mirliton to be sent to the Carolina growers.
They were successfully received in great shape on July 1st and 2nd, where they were unwrapped and potted in 3-gallon pots with a mixture of good potting mix.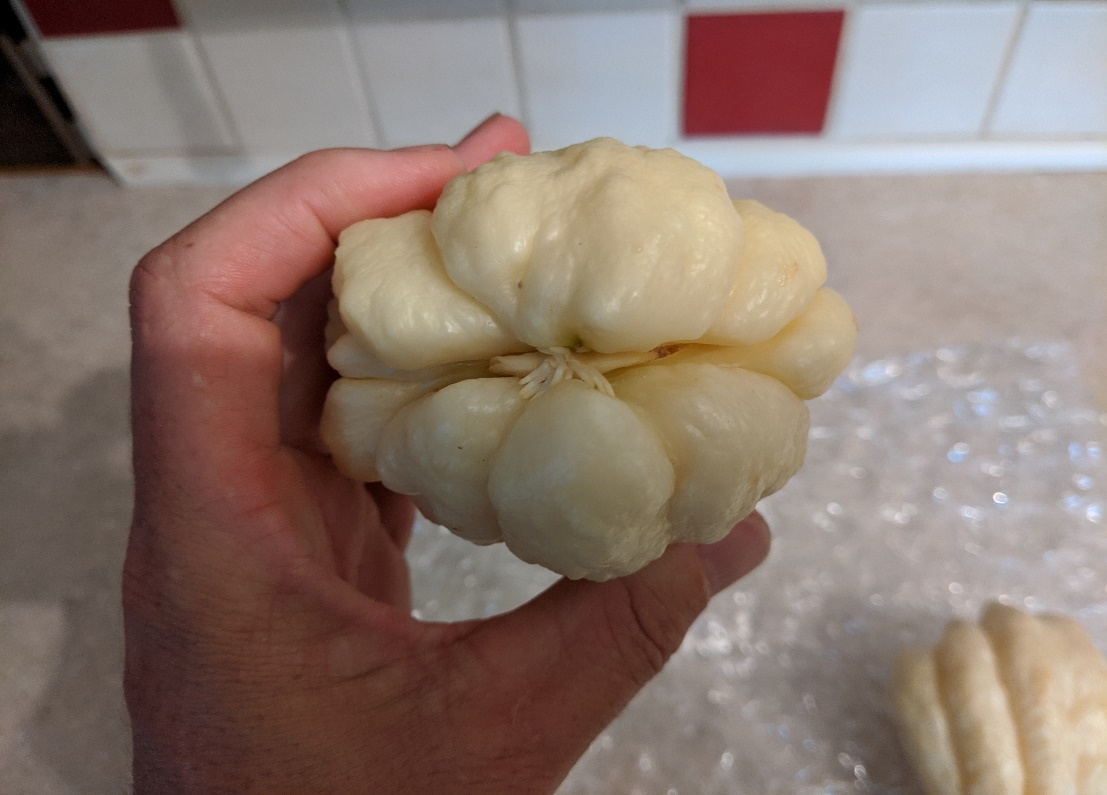 
Image 3. Recently unpacked white mirliton from Ashville, North Carolina grower, Chris Smith.
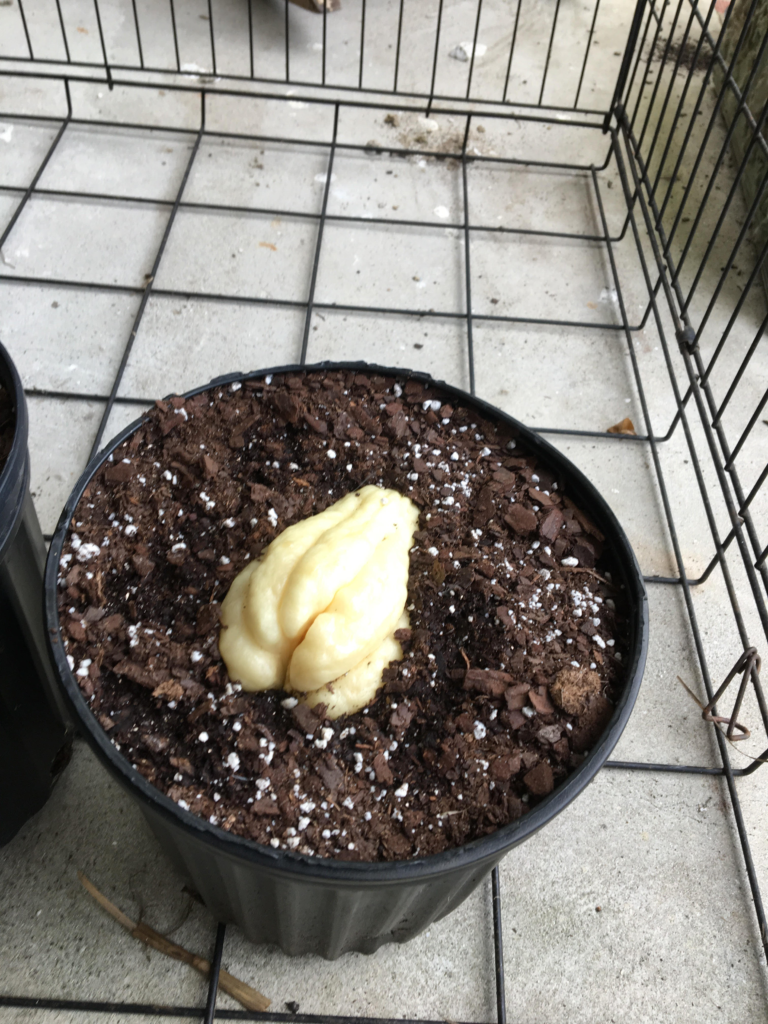

Image 4. Potted white mirliton from Columbia, South Carolina grower, Keith Mearns.
Around this same time, Houma grower James Cobb picked up his potted mirliton from Paul in Metairie.
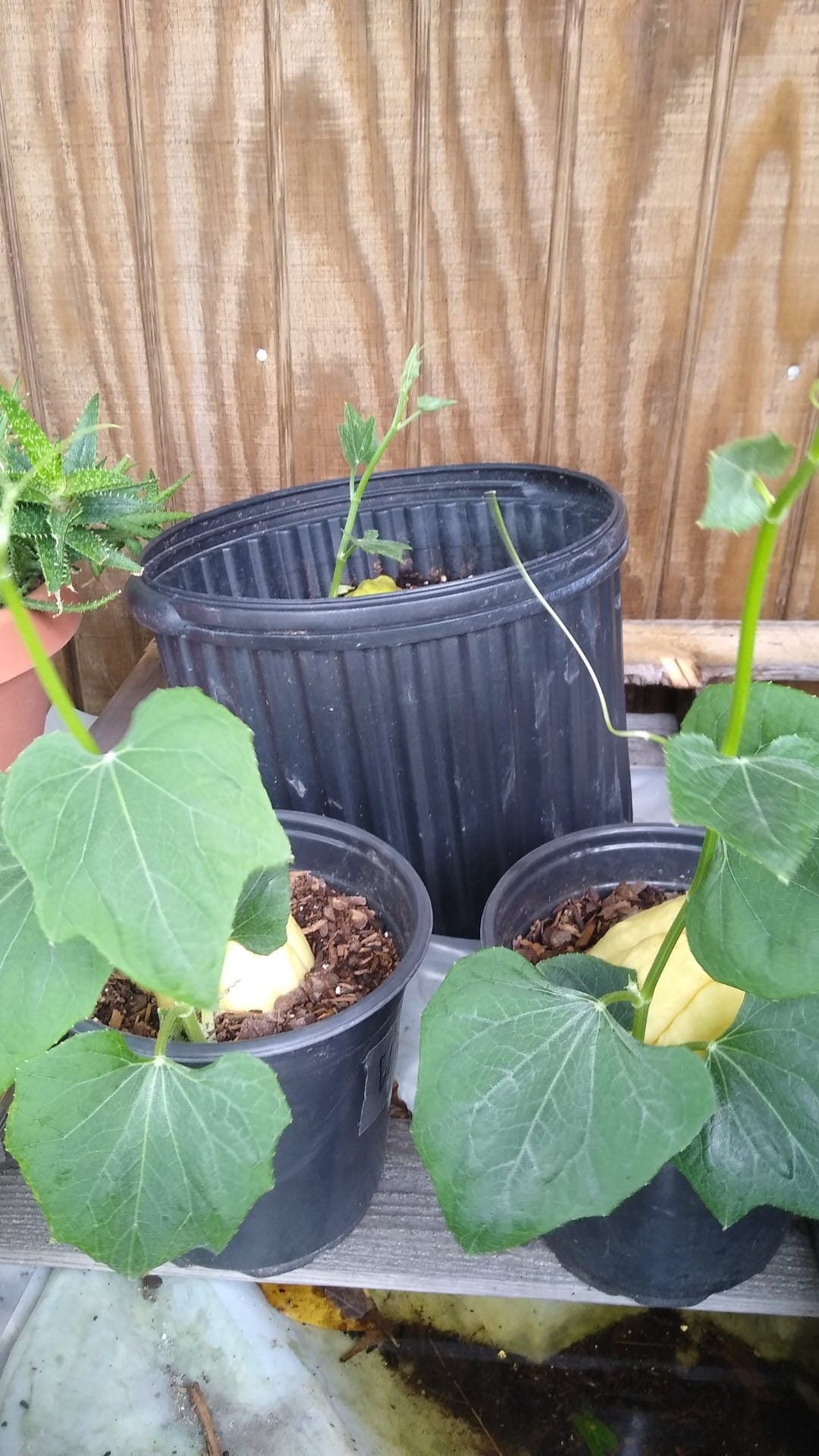

Image 5. Potted white mirliton from Houma, Louisiana grower, James Cobb.
In addition to their distribution efforts, both Paul and Chef John had potted a few of their sprouts to add to their respective gardens to further improve the 2020 Fall yields.
Additionally, Chef John and Brian put together a video to the growers in the Ishreal Thibodeaux White Mirliton Preservation Project which included a mini lesson in history and how to properly pot these seeds mirliton to ensure success.
Insurance and Experimentation:
By July 7th, the core group of first round growers had all received their mirlitons. Since there were some sprouts still remaining, it was decided these would be potted as a bit of insurance in case we encounter any issues before September. If all goes well, any remaining plants not needed in September will be sold to the next round of growers.
Due to the extra sprouts that they had saved, both Paul and John decided to experiment with direct planting into the ground, but both took added precautions to ensure success the intense 98-100 degree heat south Louisiana has been experiencing. In Paul’s case, he planted his in a partially shaded area of yard. John and Brian installed a shade cloth to protect against the heat and their efforts have paid off with three vines having sprung up thus far. Chef John notes “The intense heat has definitely played havoc on the new plantings and we really have to nurse and protect them daily from getting burned up.”
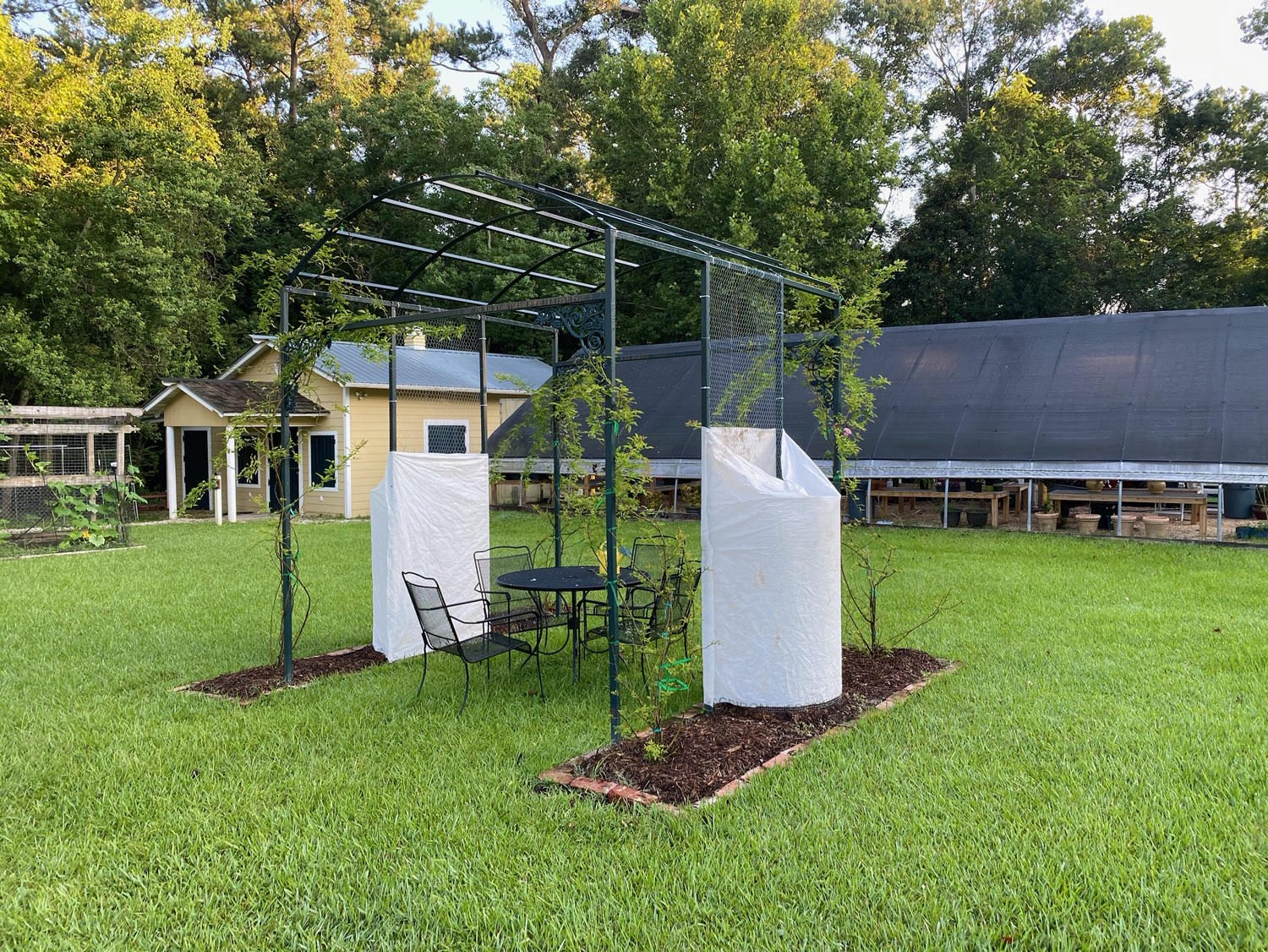

Image 6. Direct planted white mirliton with protective shade cloth at White Oak Estate and Gardens in Baton Rouge.
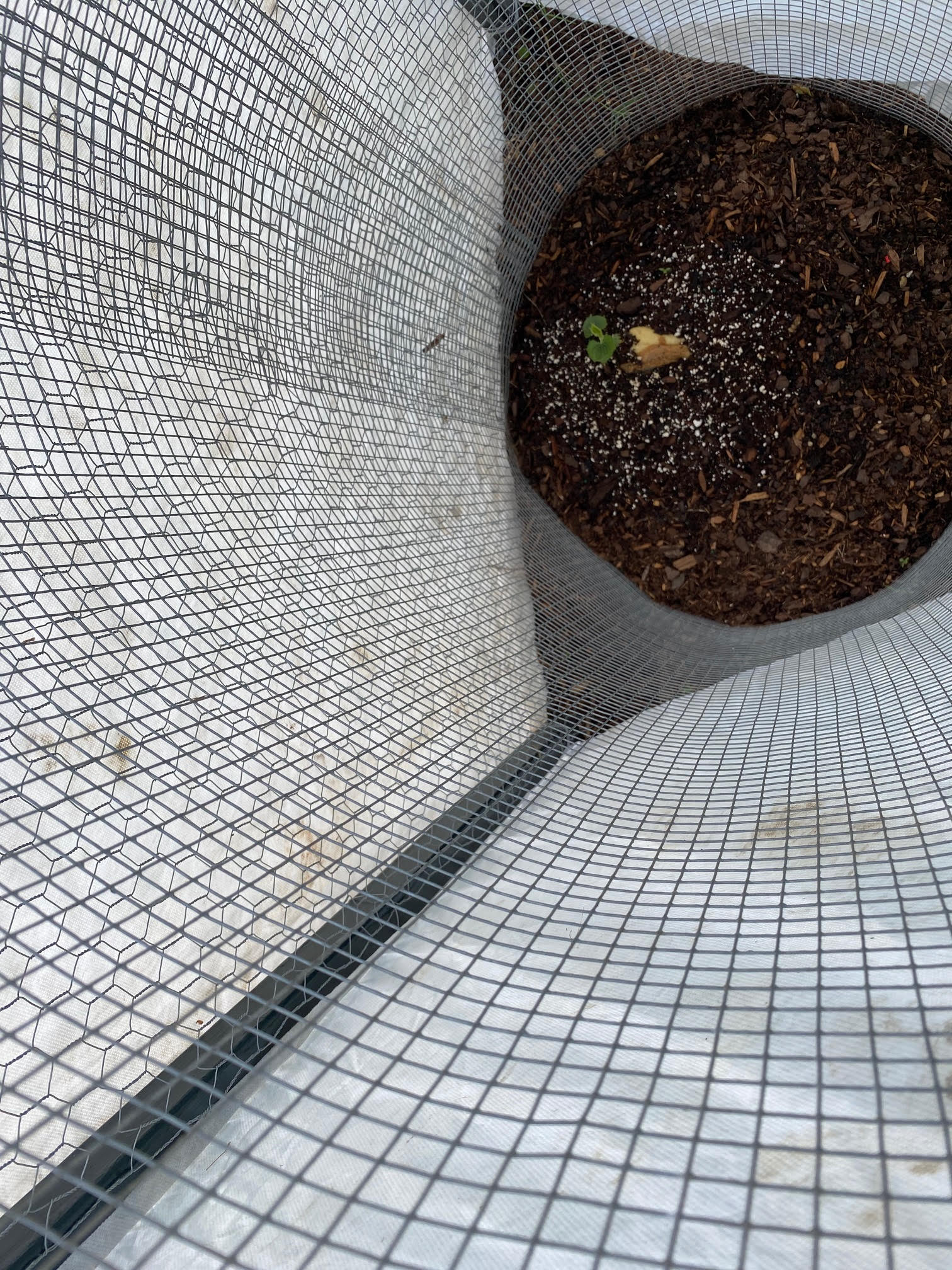

Image 7. Direct planted sprouting white mirliton with protective shade cloth at White Oak Estate and Gardens in Baton Rouge.
Some additional growing notes I would like to pass on from Chef John are “The White mirliton is definitely affected by the late June to mid-August heat. The mirliton seems to whiter and develops brown spots and begins to rot in this high heat. The mirliton once picked really needs to sit in a cool dark space (I put them in my bottom desk drawer to stay cool and dark until I started to see roots and vine sprout.) I then moved them out for planting. Next year however, I will definitely not rush this process. I’ll leave them in a cool, dark space until I have a nice vine growth 6-10 inches them plant under shade cloth to help establish a healthy plant.”
Education and Inspiration Through Food:
Shortly after we announced the Ishreal Thibodeaux White Mirliton Preservation Project, I was invited to appear on the local Mobile gardening radio show about the planned efforts. Mobile’s horticulturist, Bill Finch, is a great supporter of the traditional Gulf Coast vegetables and is very interested in mirliton. I am including the link to the show for those interested. The discussion starts around 23 minutes in:
https://fmtalk1065.com/podcast/plain-gardening-show-with-bill-finch-6-21-20-hour-1
This was then followed by an invitation to appear on July 5th on another Mobile radio show, Sip and Chew with Mike and Stu to discuss the project, as well as to learn more about mirliton in general. To help with the discussion, I brought them some food samples to help “educate their palates” on mirliton. Once again, if interested here is the link to the show as well as one of the dishes I prepared for them. The discussion lasts from 15-34 minutes:
https://audioboom.com/posts/7625135-sip-and-chew-7-05-20?fbclid=IwAR2zMJ2-FxvKrJXvvUp1BhnBh4qfAiCxMch0O0DNrf-bRQGD6dYssIetQmo

Image 8. Mirliton, Andouille, & Gulf Shrimp Dressing ala Mobile, Alabama. Recipe in link https://youtu.be/g14oA1nmJ7Y
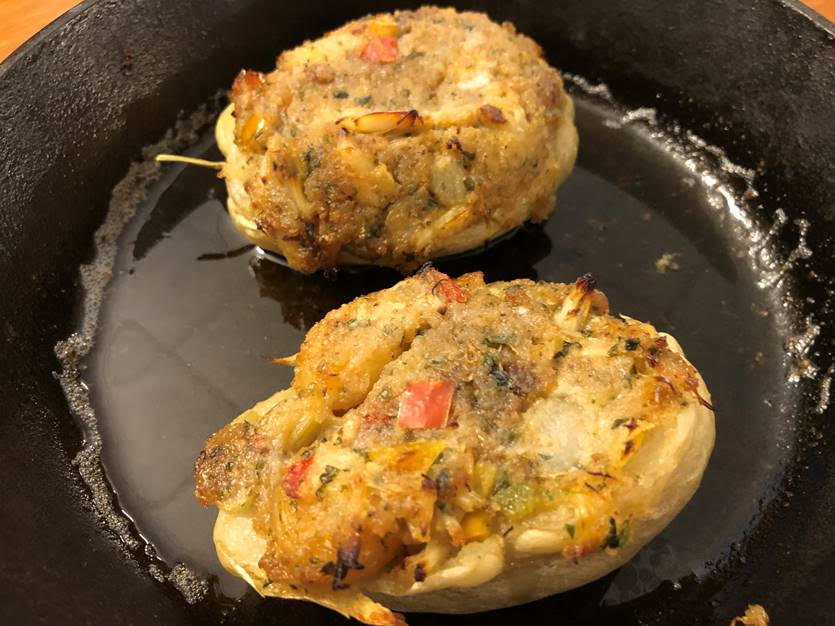
Finally, on July 24th, my family and I visited Chef John at White Oak to check on the progress of his original vine and see how the potted seed mirlitons were doing. In addition, he and I took one of his few remaining Ishreal Thibodeaux white mirlitons from this spring harvest and prepared one of his classic mirliton recipes. Attached is the link to the video of our work so the readers can see why we get so excited about preserving the white mirliton and mirlitons in general. https://youtu.be/trMlF_fu_CE

Image 9. The original white mirliton vine at White Oak Estate and Gardens in Baton Rouge is still continuing to thrive through the hot July weather.

Image 10. Chef John Folse’s Crabmeat- and Shrimp-Stuffed White Mirliton https://youtu.be/trMlF_fu_CE
Closing Thoughts for Effort So Far:
This update will be the first of many to come, hopefully monthly, to detail the subscribers to Mirliton.org on the progress being made to restore the Ishreal Thibodeaux variety. As you can see, the team of growers have been quite busy since we announced the project. As we go into August, we along the Gulf Coast will be especially on guard to protect these plants to ensure they make it through perhaps the hottest and most brutal month for us. Rest assure that all on the project will do their utmost to get through this time so that we are able to transfer the potted vines into the soil and focus on hopefully what will be a successful but possibly small first crop.
If you have any comments, questions, or suggestions, please send them to me David J. Hubbell at rpcajun2r@gmail.com. Thank you.
by Lance Hill | Dec 6, 2019 | Mirliton
The following blog was submitted by David Hubbell from Mobile. I asked him to explain how he saved his family heirloom mirliton from the recent early freeze, the worse one in 112 years. Every year we are losing locally grown varieties because of climate changes; droughts, early frosts, intensive precipitation events and flooding. If we are going to preserve out heirloom varieties, we need to plan for these challenges. David started from the beginning with a trellis he could easily and quickly protect from the frost or freeze. The old saying was that mirlitons take care of themselves; they use to, but not anymore.
Lance
Freeze Protection for Mirlitons
By David Hubbell
To say I was a bit concerned when I received an email titled “Frost Alert…” from mirliton.org on November 8th is a bit of an understatement. In Mobile, Alabama the typical first frost dates are November 21st-30th, which is what I have typically experienced over the past 10 years of growing mirlitons here. However, to get down below freezing for more than 6 hours and nearly two weeks early was almost unprecedented. Of course, we have had similar predictions in the past that would change as the forecast got closer to the predicted date, however, the local experts were telling us this one was serious.
On the following Sunday, I tuned in to the Plain Gardening with Bill Finch, our local gardening guru on the radio, to get his take on the forecast. Just like mirliton.org, Bill was extremely concerned on what was going to happen to the fruits, vegetables, and ornamental plants of the area should we see the predicted 12 hours of 25-29 oF temperatures. Bill is also a great supporter of the mirliton effort and we have spoken frequently over the last several years on the subject. In fact, he even lamented on the air “what was David Hubbell going to do with his mirliton?”
So, what was I going to do? Well, evaluating the situation and looking over my experience of the last 10 years I figured I had at least three possible options:
-
Cut the vine back to 2” above the surface and cover with mulch
-
Try the sprinkler method suggested by Lance Hill at mirliton.org or
-
Try to provide enough cover and heat
Since I had only picked two mirliton and had a lot of blooms with plenty of growing time left, I decided against option 1. While option 2 made logical sense to me, the area of my structure and the types of sprinklers I had didn’t lend themselves to this method; plus, due to the proximity to my driveway I may actually be creating a slipping hazard with the water. Therefore, I decided by default to go for option 3. I had some previous attempts at this over the years with mixed success and I had somewhat designed my mirliton support structure for such an enhancement.
Preliminary Steps
Before even considering protecting against a freeze, I had planted my vine in a well-drained location about 25 feet away from a big water oak with a decent canopy. This location is also heavily shaded by some of the neighboring trees and even three navel orange trees I planted nearby around the same time. Unbeknownst to me at that time, this probably has provided a bit of an infrastructure needed to help keep heat released from the ground trapped beneath the canopy and warm the mirliton vine. The first few years of growing mirliton was basically trying to mimic visions I had of old T-pole clothes lines I thought I remembered seeing mirliton grow on as a kid. I did this with a nice, but inadequate trellis and a long rope tied to the water oak. After the massive amount of plant growth during the first few years I realized I needed a “beefier” structure. Seeing pictures of similar structures created from folks in the New Orleans area I choose to create a system with six 4×4 posts separated by 1×4-12 planks lengthwise and 1×4-8 widthwise, and using reinforcing wire and small 1×2 railing pieces on top (see Figure 1.) The main advantages of this structure for me was a place for the vines to grow across the top while allowing the fruit to hang down so I could easily walk under it and inspect and pick. Plus I know had a structure that could now be easily reinforced with coverings and heater/heat lights if needed.
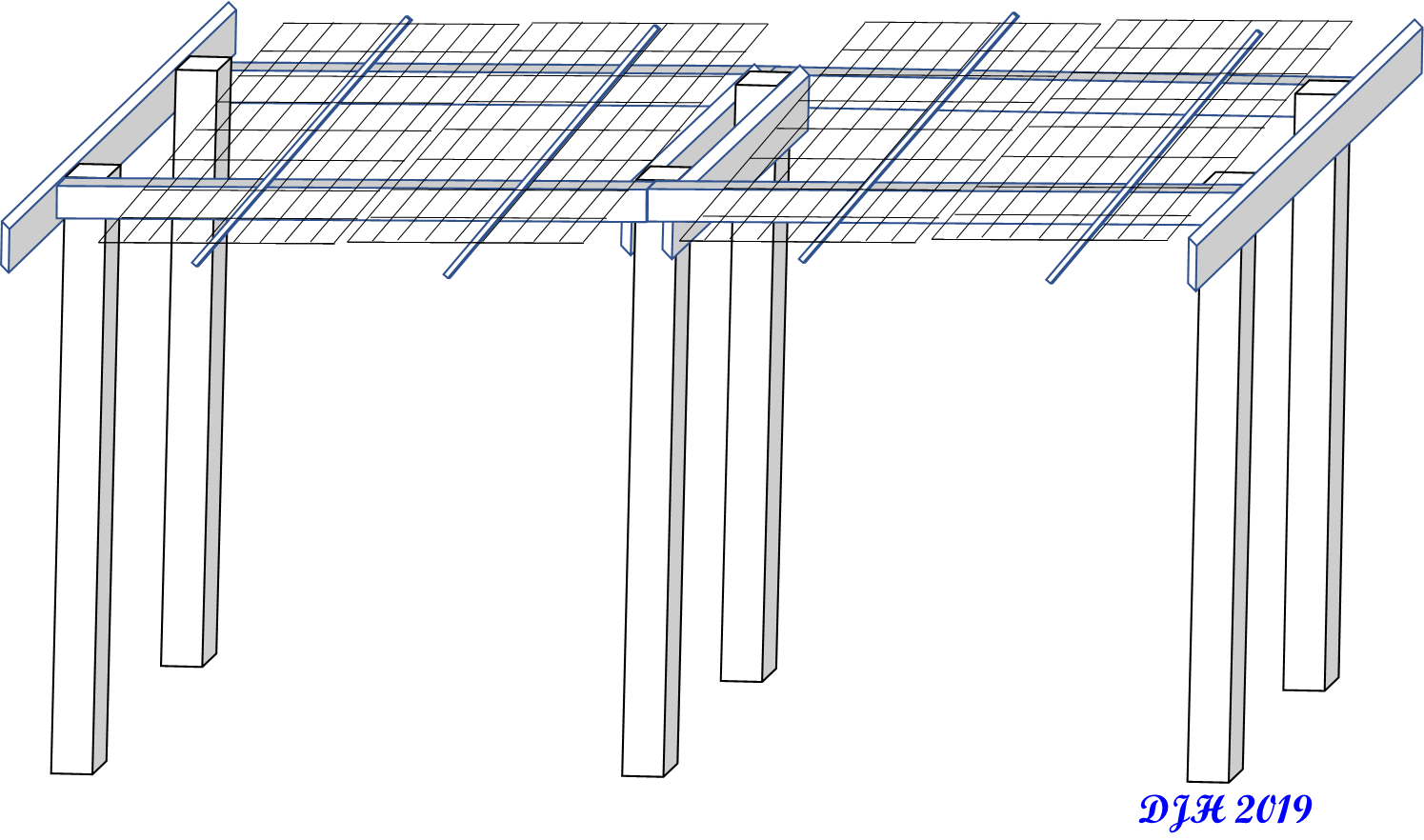
FIGURE 1. Mirliton Structure
Materials Used for Freeze Protection
-
20 ft. x 25 ft. Clear 4 mil Plastic Sheeting – quantity 2
-
Old flannel King Size Bedsheets -quantity 4 (more preferable)
-
Heavy Black Yard Bags full of leaves – quantity 5 (more preferable)
-
Incandescent Heat Lamp – quantity 1 (2 or 3 may be preferable)
-
Halogen Lamp – quantity 1
-
360 Surround Indoor Heater Black 1500W – quantity 1
-
Swimming Pool Cover – 15 foot diameter – quantity 1 (3 or more preferable)
-
½” thick plywood -enough to cover top
-
Clamps of various size
Freeze Protection Steps
Two Days before predicted frost:
-
Rake all of the leaves and loose material away from the mirliton structure. This will allow as much heat to absorb into the ground, which will in turn be released back at night during the freeze.
-
Fill as many black plastic yard bags as possible and allow them to absorb the heat from the sun.
-
If your vine has grown beyond the structure, pick any mirliton that are of a useable size on that part of the vine, then pull all of the vines up under the structure. In my case this basically killed this portion of the vine, but the plan is to protect the main plant as much as possible, so for me this turned out to be somewhat of a sacrificial act.
Day before predicted frost:
-
Place black plastic bags around the base of the vine to form an insulating barrier from the cold.
-
Cover leaves and vines with as much flannel or thick cloth as possible. NOTE: You don’t want the plastic material to directly touch the leaves. There will still be damage without the cloth and only the plastic.
-
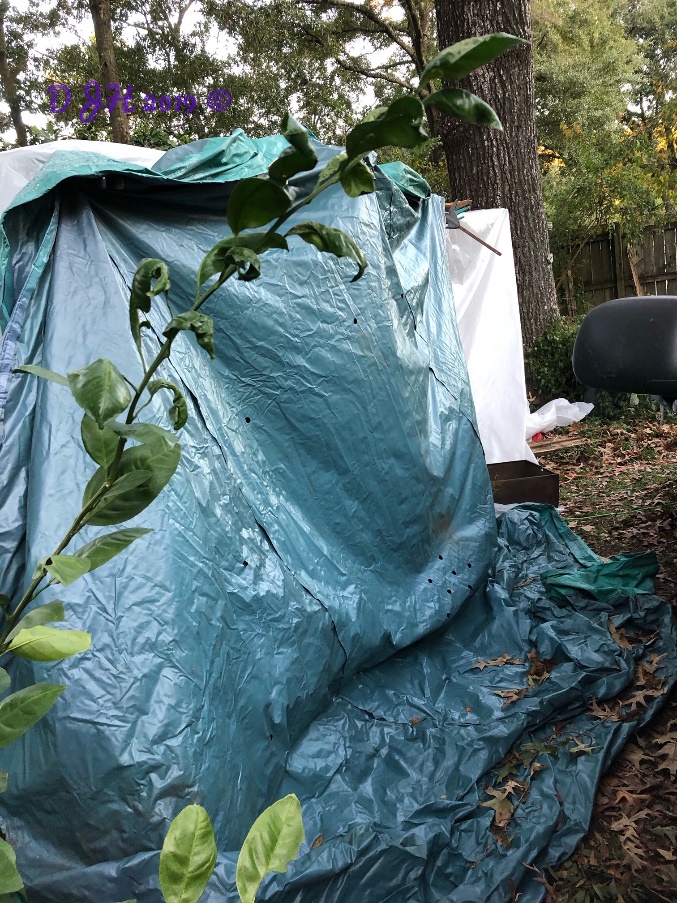
With assistance, take one of the 20 ft. x 25 ft. clear plastic sheeting and cover the cloth allowing about a 2 foot over lay onto the ground to prevent a way for the cold air to “short circuit” the protective barrier. Use as many clamps as possible to secure to the wooden structure.
-
Repeat with other roll of plastic in a similar manner. NOTE: If your structure is bigger, you may need more rolls.
-
Once again with an assistant’s help, cover the structure with the pool cover(s) especially if you didn’t have enough sheets to cover the plants.
-
Position heat lamp(s), light(s), and heater. NOTE: Do not place them directly against and cloth, plastic, vegetation, or dried vegetation. This could cause a fire to the structure or heat damage to the plant.
-
Place plywood on top of the structure. This serves three purposes:
-
Added insulation
-
Traps in heat from lamps/heater.
-
Protection from rain. In my case, rain was predicted with the incoming cold front. In years past I learned that the rain will collect on the plastic and cause the barrier to be breached thus thwarting all of your efforts.
-
Finally, place heavy objects such as pots full of dirt, bricks, cinder blocks, etc. around the over hanging plastic to ensure the winds doesn’t gust up underneath. Also secure any openings where the cords going to the lights or plastics overlap with smaller clamps. Try to make the covering as secure and tight to prevent any breaches of cold air.
Day after predicted frost:
-
Once freezing temperatures have passed and outside conditions get in the mid-30s oF, unplug heat sources.
-
Remove as much as covering as possible so as not to damage the plant now that danger of frost and freezing has passed. At a minimum open up enough to allow ventilation of the mirliton vine.
-
Inspect the plant for damage.
-
Water the vine and apply a gallon of a water-soluble vegetable fertilizer.
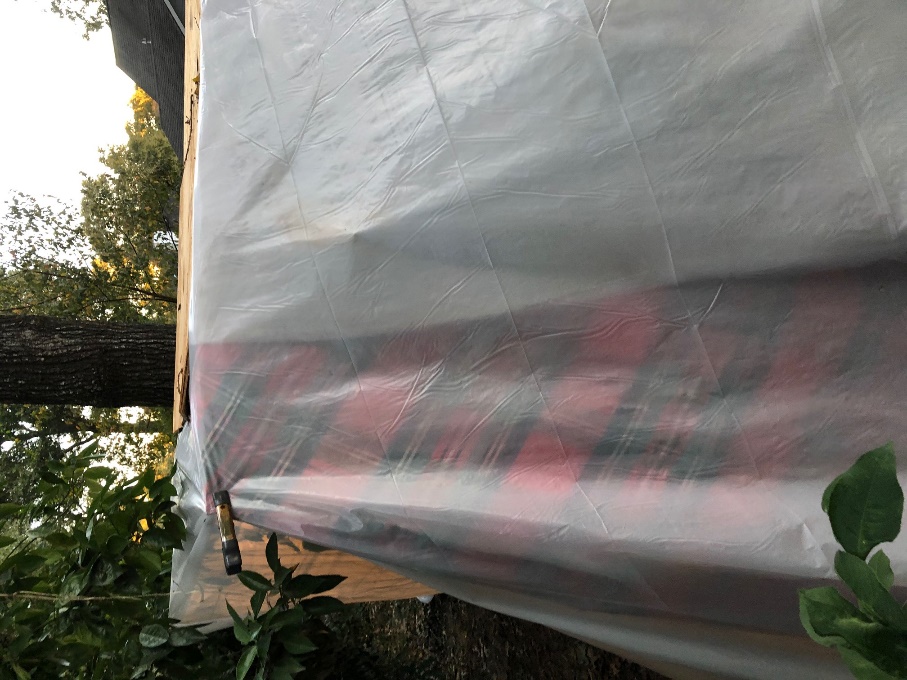




Final Thoughts
The previously describe method was based off of my 10 years of mirliton growing experience. I feel I was quite fortunate to have escaped any significant damage. I would like to add that if the freezing temperatures would have been predicated for more than 12 hours, I would have been hard pressed to try either methods 2 or 3. While it is nice to extend the growing season for the mirliton, I feel it is more important to preserve the Louisiana heirloom varieties as best as possible. In the case of prolonged freezing weather or after the typical fruiting season has passed (mid December) that means method 1. While it is always a sad day at the Hubbell Household when I have to cut the mirliton vine back, I know that by March I will start to see sprouts returning and if I am lucky will be treated to a small springtime crop.
Thanks for taking to time to read my thoughts and please feel free to contact me at rpcajun2r@gmail.com.
by Lance Hill | Nov 8, 2019 | Mirliton
Frost Alert for Next several Nights
by Lance Hill
The forecast calls for temperatures below 40 f. for the next several nights and in the high 20s on Tuesday night. If you have a vine, you can save it using an overhead rotary sprinkler as show on the “Photos” page under “Frost Protection Sprinkler Systems.” Simply turn the sprinkler on at sunset and then off in the morning. It can protect a mirliton vine down to about 29 degrees. If you don’t choose to use a sprinkler, than cut the vine back to the base and place some carpet and heavy mulch over the crown. About once a month you need to replace the carpet and mulch to prevent disease and pests until next spring.
I don’t get any reports of a good crop this year because the drought has disturbed normal flowering and now we have the early frost. But that’s what makes mirliton growing so rewarding; only the careful, attentive, and knowledgeable gardener succeeds. The tribulations are many but the rewards a great.
We have just added several hundred recipes to our “Mirliton Recipes” page, which is the largest collection of international mirliton/chayote recipes in the world. Yes, the world! Go to the page and scroll down to “Recipes added September 23, 2019” to see the new recipes.
Divinely yours,
Lance Hill
by Lance Hill | Aug 15, 2019 | Mirliton
As we head into the final month before the beginning of fall flowering, it’s a good time to pause and prepare. Our method of gardening is the “worse-case event” technique; the old saying that “mirlitons take care of themselves” is no longer true. Due to changing climate, mirlitons need an attentive caregiver. The best way to nurture mirlitons is to plan for all predictable events even if they are improbable. The summer heavy rains and intense heat have stressed plants, but here are some tips to anticipate the possible problems and ensure a good harvest.
Monitor your vines daily. Nothing is better than spending some quality time with your mirliton scouting for pests, disease, and watering problems. As my friend and mirliton expert grower Paul D’Anna says, get your morning cup of coffee and visit your vine daily.
Diseases. This is the time for the plant disease anthracnose which thrives on high heat and moisture. Colletotrichum lagenerium, the fungus that causes anthracnose, is a global problem and there is no effective organic treatment for it. But generally plants that suffer some die-off in August normally recover in September and fruit. Remove the yellowed and dead leaves and place in a plastic bag and dispose. Here are some photos and FAQs on the disease:
How to Diagnose Anthracnose
Anthracnose infected leaves
Wilting Anthracnose
Not all wilting is caused by anthracnose. Mirlitons will naturally wilt during the day in July and August yet they recuperate at night when they normally uptake water. Drying out actually toughens the leaves and protects them from disease. To diagnose soil moisture problems, look for traces of guttation and use a bamboo stake to test soil moisture daily.
Insects. Leaffooted stink bugs tend to show up for mirliton buffet once flowering starts. See examples of juvenile and adult bugs here. They are tough critters and mature bugs are impervious to insecticides, but they can easily be picked off with a butterfly net or a hand vacuum. I use a portable 20 volt vacuum with a PVC pipe extension (grandkids love to suck up pesky bugs), but a cheap butterfly net will suffice. Again, remove the bugs to a bag and dispose. We are experimenting with a “trap crop” strategy to divert stink bugs and will report out soon.
Pollinators. Mirlitons need honey bees to fruit but bees are scarce these days, especially in cities that experienced flooding and hurricanes that ruined bee habitat. A bee keeper told me he removed hundreds of hives while re-roofing houses damaged by hurricane Katrina. That was their favorite home in the city. If you don’t see bees visiting your mirliton flowers about midmorning when bees normally forage, you have two options. One is to hand-pollinate which is easy and fun. See the technique here. Second is to apply a bee pheromone like Beescent in September-October to attract bees. There are no studies on mirlitons and bee attractants, though some research shows they are effective with specific crops. I will offer you the worst kind advice gardening advice on the subject; I tried it and it works for me.
Weave your vine. High winds can traumatize vines and disturb flowering. The solution is simple; as the vine grows, weave the tips of vines through your trellis so that it secures itself to the wire trellis. Best to do this throughout the whole growing season, but it’s never too late to start.
Install a sprinkler system now while it is hot and fun to get wet while setting it up. A cheap rotary sprinkler activated when temperatures are forecast to drop below 40 degrees f. at night will protect your vine from early frost. The method works, saving mirlitons through September to November cold snaps. See a simple rotary sprinkler mounted above a trellis here and a ground-mounted sprinkler here.
by Lance Hill | Aug 2, 2019 | Mirliton

Renee Lapeyrolerie, proud grower in Treme neighbor of New Orleans
As a young girl in St. John Parish, Louisiana, Renee Lapeyrolerie lived in a community in which mirlitons were a common site in back yards. When she moved to New Orleans to attend Loyola University, she soon began to yearn for the lush growth of the vine. 20 years ago she bought a home in the centuries-old African American neighborhood of Treme (pronounced, Tra-May), a famous community of free people of color, many of them migrants from Haiti, and including a maternal ancestor who bought property in 1795. Haitians brought mirlitons with them from their new nation, an integral part of Haitian cuisine.
Parts of the Treme flooded during hurricane Katrina, but only a few feet. The community was part of the slim alluvial ridge along the Mississippi river and was home to mirliton gardeners for decades.
About five years ago Lapeyrolerie (pronounced Lap-a-rol-er-y) purchased a mirliton sprout from a garden center and planted it in her back yard. The vine soon spread about 20 feet along her fence and began to charge up her neighbor’s tree. Its origins as a variety are uncertain, but it is definitely part of the Louisiana landrace because it fits the phenotype (large but uniquely without furrows) and it has proven it can flourish in our climate. In the early years she had some problems with the vine flowering but not fruiting. This was not unusual for New Orleans post-Katrina because the flooding and re-roofing destroyed the habitat for bees (many hives were in attics that were disturbed by roofing). She is considering using a synthetic bee pheromone to attract bees this fall, though she can hand pollinate using instructions on our photo site.
In recent years, her five year old plant produced a good fall crop and she even got a modest spring crop in 2019. For advice on the culture of the plant, Renee had only go to her Aunt Helen and neighbors back in St. John Parish. Renee hopes to inspire fellow Treme residents to take up the mirliton and renew a tradition that is two centuries old and has donated several sprouts and plants to Mirliton.Org.
We have named the variety the “Lapeyrolerie Mirliton Variety” in honor of Renee.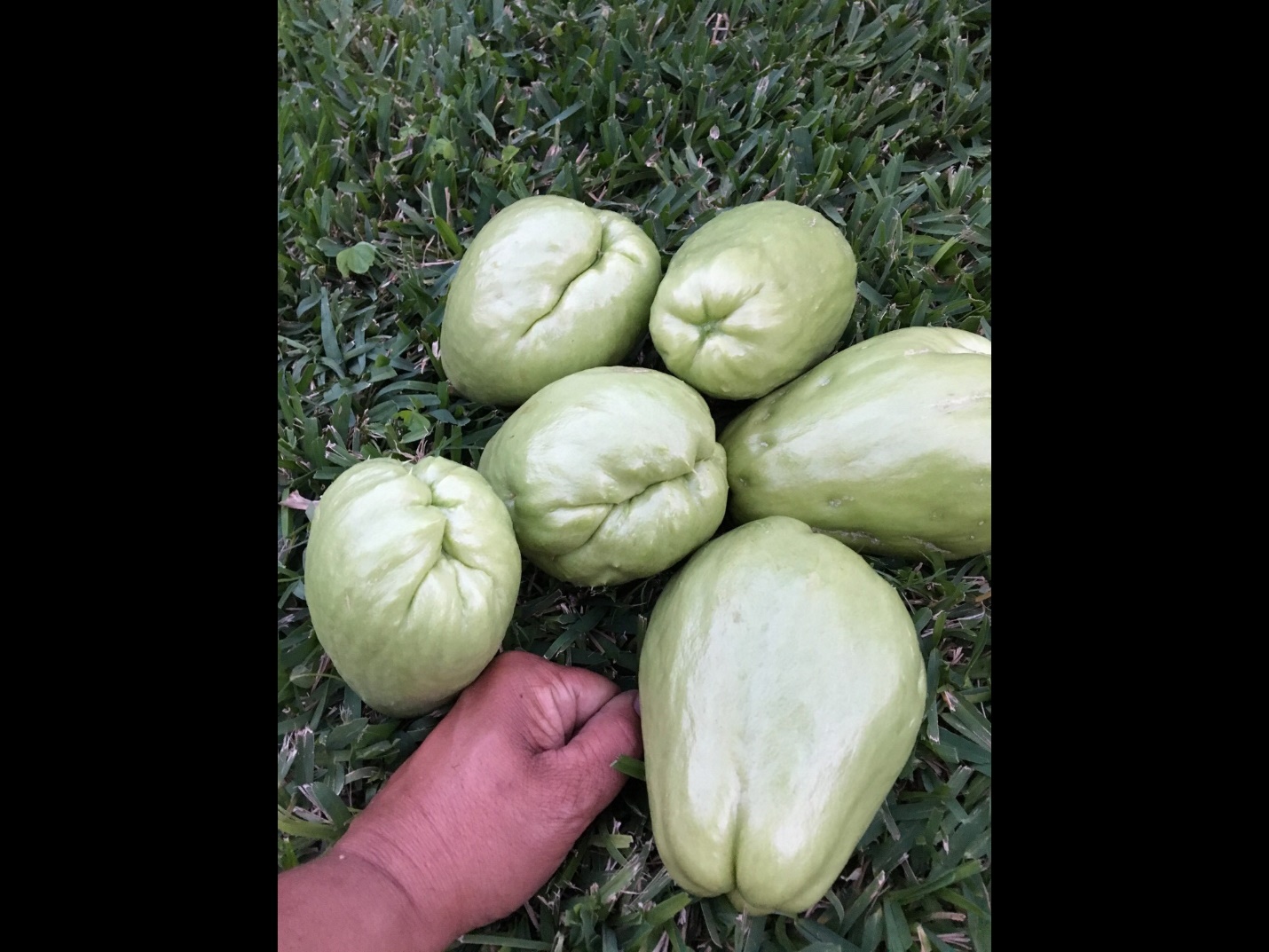  Lapeyrolerie Mirlitons
Lapeyrolerie Mirlitons
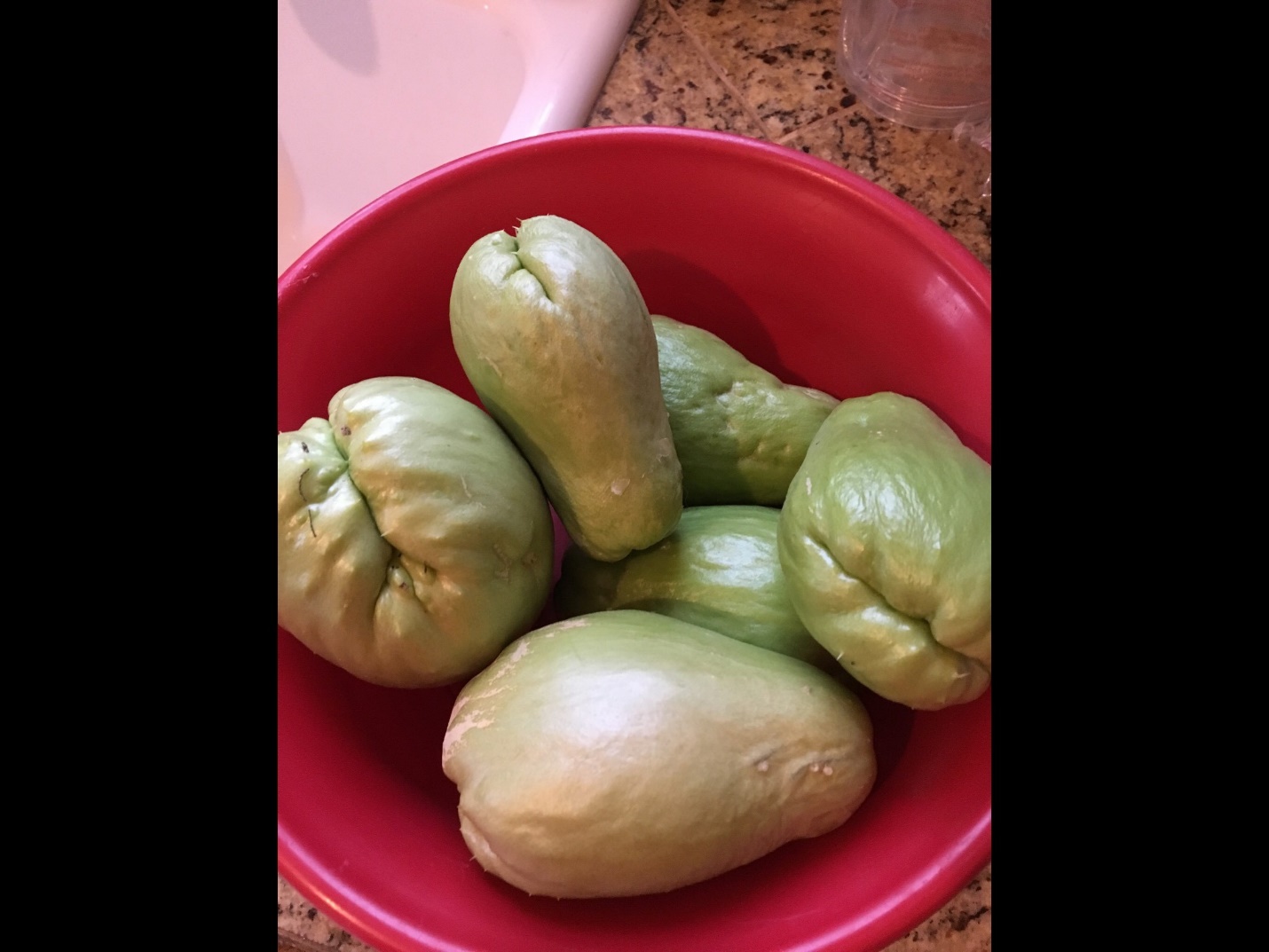

Lapeyrolerie Mirlitons
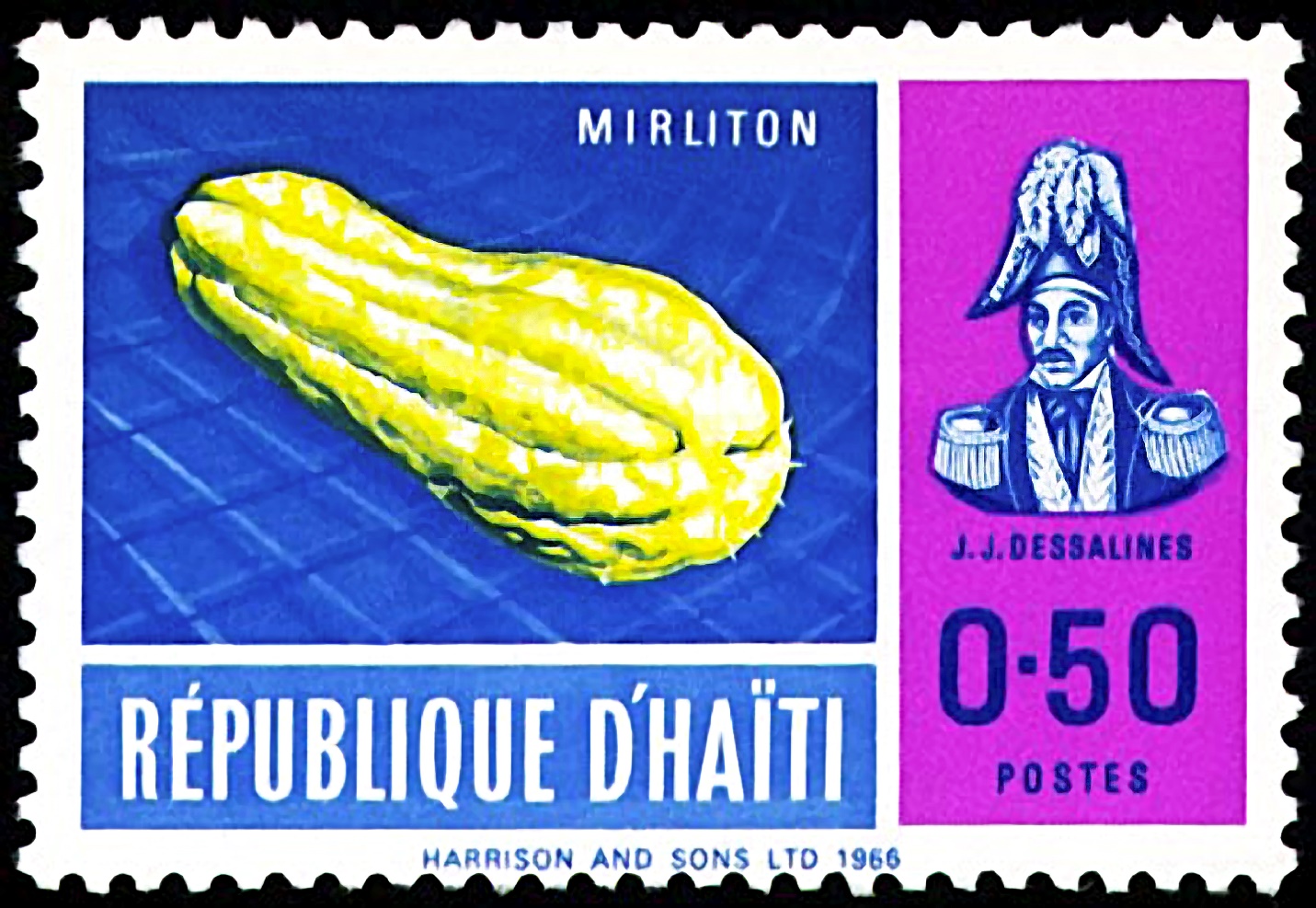

1 Haitian postage stamp, circa 1966

Renee Lapeyrolerie, proud grower in Treme neighbor of New Orleans
As a young girl in St. John Parish, Louisiana, Renee Lapeyrolerie lived in a community in which mirlitons were a common site in back yards. When she moved to New Orleans to attend Loyola University, she soon began to yearn for the lush growth of the vine. 20 years ago she bought a home in the centuries-old African American neighborhood of Treme (pronounced, Tra-May), a famous community of free people of color, many of them migrants from Haiti, and including a maternal ancestor who bought property in 1795. Haitians brought mirlitons with them from their new nation, an integral part of Haitian cuisine.
Parts of the Treme flooded during hurricane Katrina, but only a few feet. The community was part of the slim alluvial ridge along the Mississippi river and was home to mirliton gardeners for decades.
About five years ago Lapeyrolerie (pronounced Lap-a-rol-er-y) purchased a mirliton sprout from a garden center and planted it in her back yard. The vine soon spread about 20 feet along her fence and began to charge up her neighbor’s tree. Its origins as a variety are uncertain, but it is definitely part of the Louisiana landrace because it fits the phenotype (large but uniquely without furrows) and it has proven it can flourish in our climate. In the early years she had some problems with the vine flowering but not fruiting. This was not unusual for New Orleans post-Katrina because the flooding and re-roofing destroyed the habitat for bees (many hives were in attics that were disturbed by roofing). She is considering using a synthetic bee pheromone to attract bees this fall, though she can hand pollinate using instructions on our photo site.
In recent years, her five year old plant produced a good fall crop and she even got a modest spring crop in 2019. For advice on the culture of the plant, Renee had only go to her Aunt Helen and neighbors back in St. John Parish. Renee hopes to inspire fellow Treme residents to take up the mirliton and renew a tradition that is two centuries old and has donated several sprouts and plants to Mirliton.Org.
We have named the variety the “Lapeyrolerie Mirliton Variety” in honor of Renee.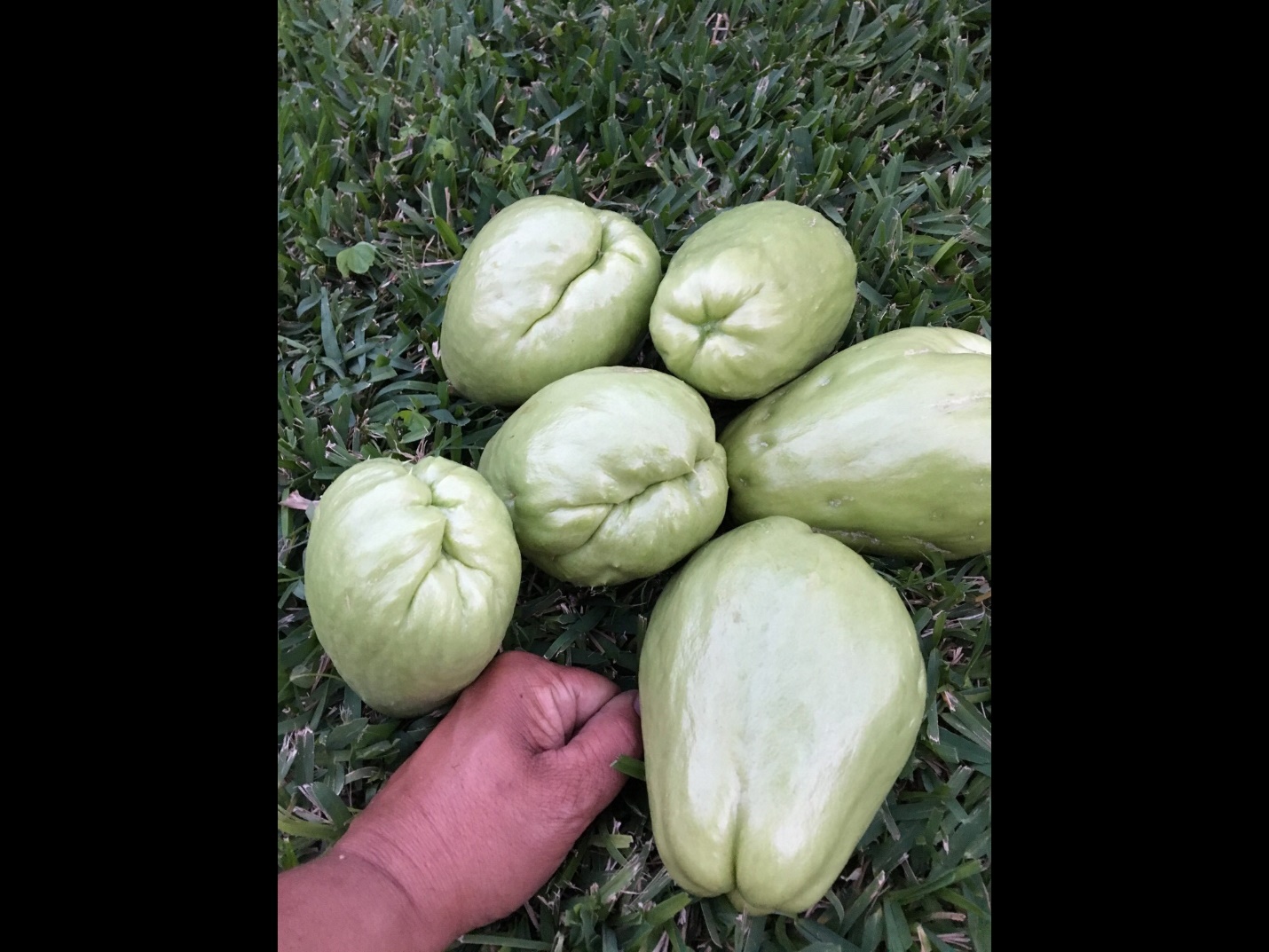  Lapeyrolerie Mirlitons
Lapeyrolerie Mirlitons

Lapeyrolerie Mirlitons

1 Haitian postage stamp, circa 1966
by Lance Hill | May 4, 2019 | Mirliton
Jason Fricke Saves An Endangered Heirloom Mirliton Variety in Texas
By Lance Hill
I had a long friendship with Jason Fricke of Pearland, Texas, a city within the Houston metropolitan area, in starting his project to be the first person to grow Louisiana heirloom mirlitons in Texas. Our email correspondence dates back nine years. Fricke was raised in New Orleans and moved to Houston, where he longed to expand mirliton growing to Texas. And there was a large demand for Mirlitons in Texas, do to the large migration of mirliton-loving Louisianans that occurred after the 2005 Hurricane Katrina.
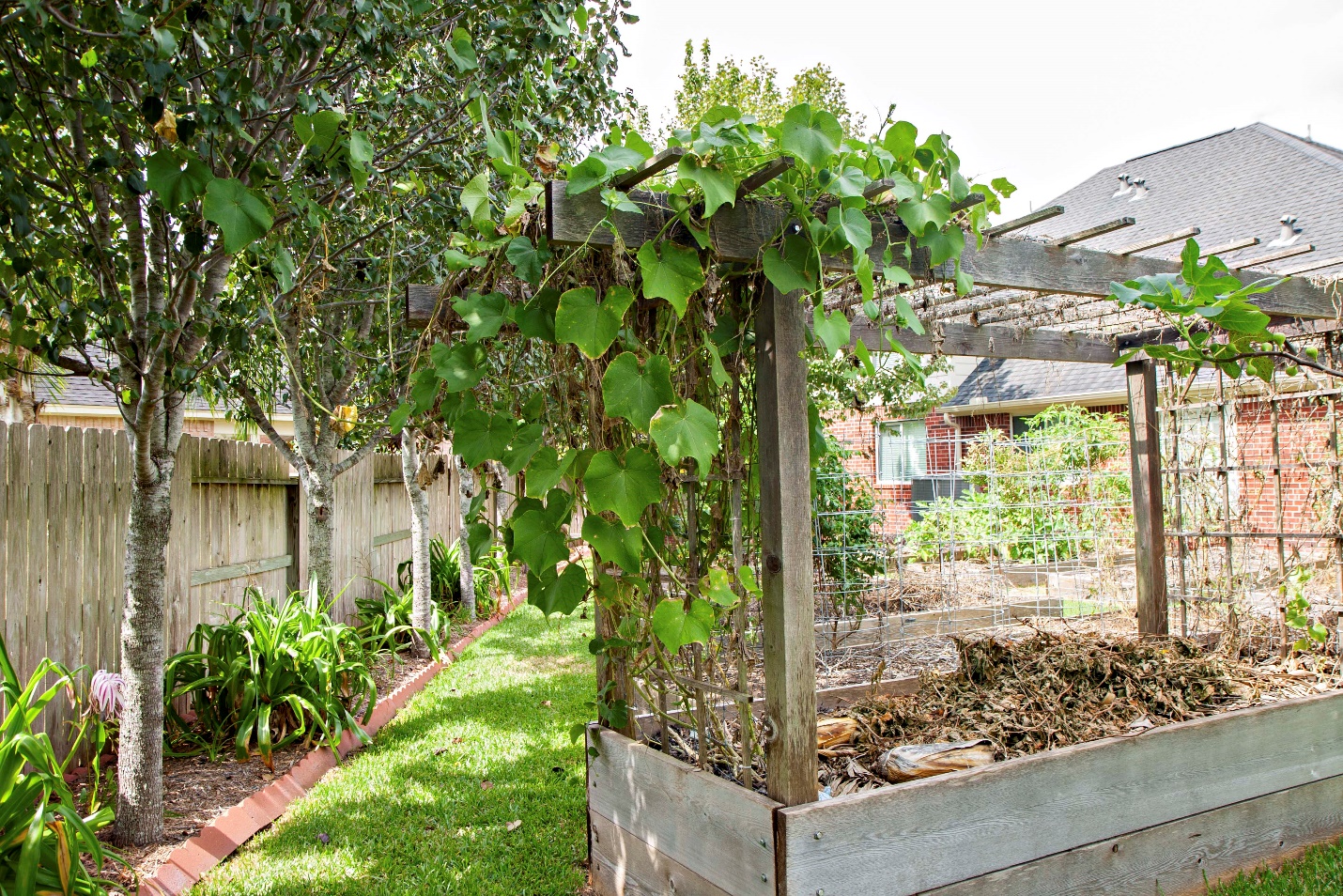

Figure 1 Jason Fricke’s mirliton site in Pearland, Texas in 2014
Fricke is a persistent and thorough gardener. He read all Mirliton.Org research and listened to our recommendations. We started out encouraging him to grow mirlitons that matched his home’s climate and altitude. South Texas is similar to hot and humid coastal Louisiana; Houston is at 43 feet altitude, nearly sea-level like coastal Louisiana, and has 53 inches of annual rainfall, also comparable to Louisiana.
The first step was to provide a Louisiana heirloom mirlitons to Fricke. The most certain way to determine if a mirliton is indeed an heirloom variety is to ask the question: was the variety locally-grown or was it purchased from a store and of unknown origin? We started by giving Fricke the “James Boutte” variety from New Iberia, Louisiana that had been grown for decades by James Boutte and his son Kevin. After a few site visits to the Boutte garden in New Iberia, the elder Boutte donated several sprouts for us to place with new growers. (see the massive Boutte vine here)
We gave some of these sprouts to Fricke and after a few years of false-starts, finally in November 2014 Fricke had success, proving that mirlitons could be grown in Texas with the right variety and proper techniques. Fricke harvested 44 mirlitons of which twenty were good seed-size and were given to fellow Texans who wanted to grow them. A few were huge and reserved to expand Fricke’s garden. The smaller ones were used for Thanksgiving dinner, as is an old Louisiana tradition. The harvest was produced by four vines located in three planting spots. The diameter of the stems at the ground were 4.5”, 4.5”, 5” and 6”.
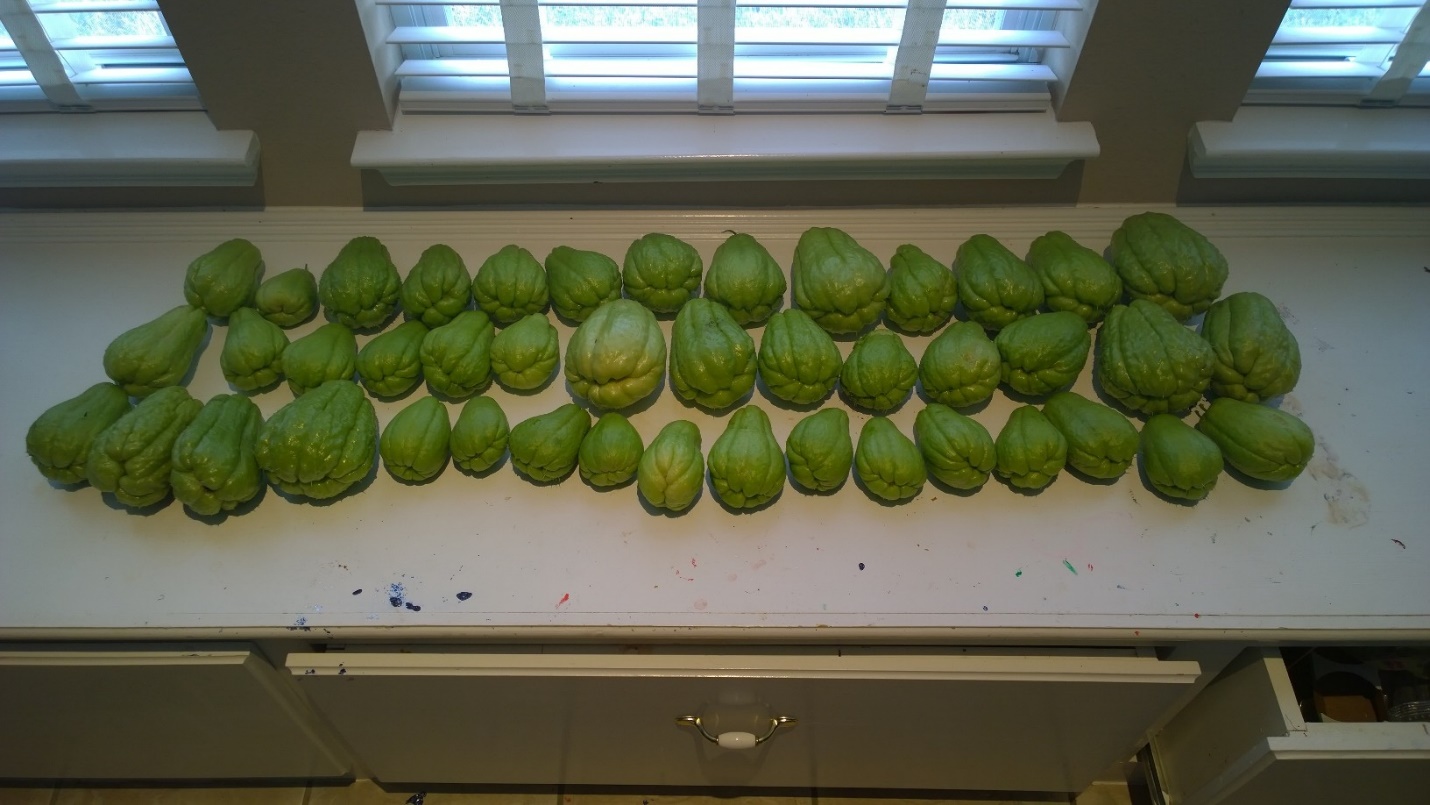

Figure 2 Fall harvest for Houston, Texas, November 2014, James Boutte heirloom mirliton variety
Originally, Fricke built a raised bed, 12″ deep and 4’x 20′ in dimensions. The problem was that the beds were not deep enough. Mirlitons don’t tolerate wide fluctuations in soil moisture content. The damping and drying-out stresses the plant and contributes to plant diseases like anthracnose. It is important that the raised bed sits on ground soil that is also well-drained. If the ground soil is soaked, the bed cannot drain properly and the raised-bed soil will also be water-logged also (bed drainage can easily be ensured by adding a perforated drain pipe to the bed, see link),
Fricke solved that problem by deepening the bed to 24”, evening out soil moisture fluctuations. He worked in sphagnum moss and used a good grade of potting soil. He placed the bed on the highest 25% of the yard, sitting on the ground soil which was a loamy clay. There was about a half-inch gap between the cedar boards and the ground soil so the whole bed was slightly raised above ground level. The bed was covered by a horizontal goat-fence trellis about 5′ above the bed.
When Fricke began growing mirlitons in 2011 he also planted cucuzza in the same bed. We advised him against growing any other cucurbit is the same garden. Cucuzza, cucumbers and other garden cucurbits are hybridized for resistance to plant fungi; that means that they can host the anthracnose fungi and while the fungus won’t kill the hybridized plants, the plants act as a sporelator spreading spores that can infect the mirliton. I have observed that successful mirliton growers grow only mirlitons and no other cucurbits to avoid this problem. Fricke removed the cucuzza and cleared the way for a healthier environment.
Fricke also began to increase his odds of success by planting multiple sprouts. It is very hard to get one or two mirlitons to grow in the first year. Multiple plantings can always be thinned out later.
In 2013, Fricke obtained 15 sprouts from James Boutte’s son, son Kevin who had taken over the vine. He learned a great deal by experimenting with different planting methods. Interestingly, out of 15 vines that Fricke started, only six made it through the summer heat of Houston. Of those original 15 vines, the three that thrived the most were planted directly in the raised beds the previous November. So starting the plants six months before in the fall was more effective than direct planting in the spring. This makes sense since a fall planting gave mirlitons several months to develop a root structure before the summer heat and rains.
Fricke had filled the beds with “Living Earth Rose Soil”, a high-quality container soil available throughout Texas, which is basically a very porous sandy soil, high in compost and organic matter. He then top-dressed the beds with his own compost and mulched a few times per year. He worked in a lot of sphagnum peat moss so that the top half of the bed was 1/3 peat. For fertilizer, Fricke added a small amount of Microlife 8-4-6 in April and some liquid 10-8-8 foliar feeding in June.
He also adjusted the watering schedule and used a drip system to try to keep the moisture levels more even. The beds drained quickly due to the sandiness, even during heavy rains. The peat moss also made a very apparent difference in moisture retention.
Now, several years into his successful mirliton project, Fricke is eager to provide “James Boutte” mirliton variety to other Texas growers.
It was none too soon. James Boutte, the scion of the variety that bore his name, died in 2015 at the age of 97. His family lost the land to the bank, so the entire mirliton farm died off.
But thanks to Jason Fricke’s determined and creative work, the “James Boutte” variety survives in its new home in Texas.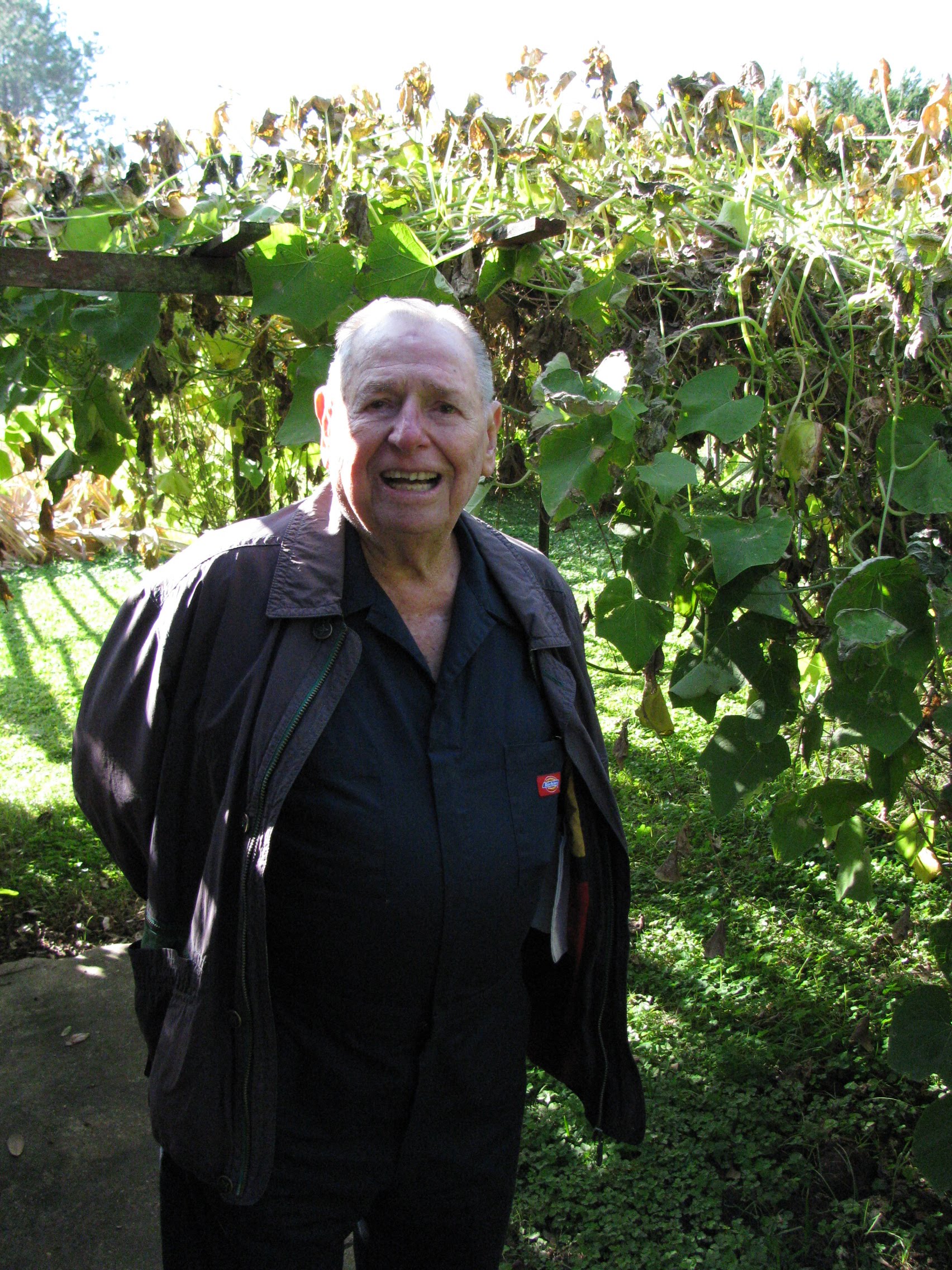 
Figure James Boutte. New Iberia, Louisiana, 2010. Boutte died in 2017.

















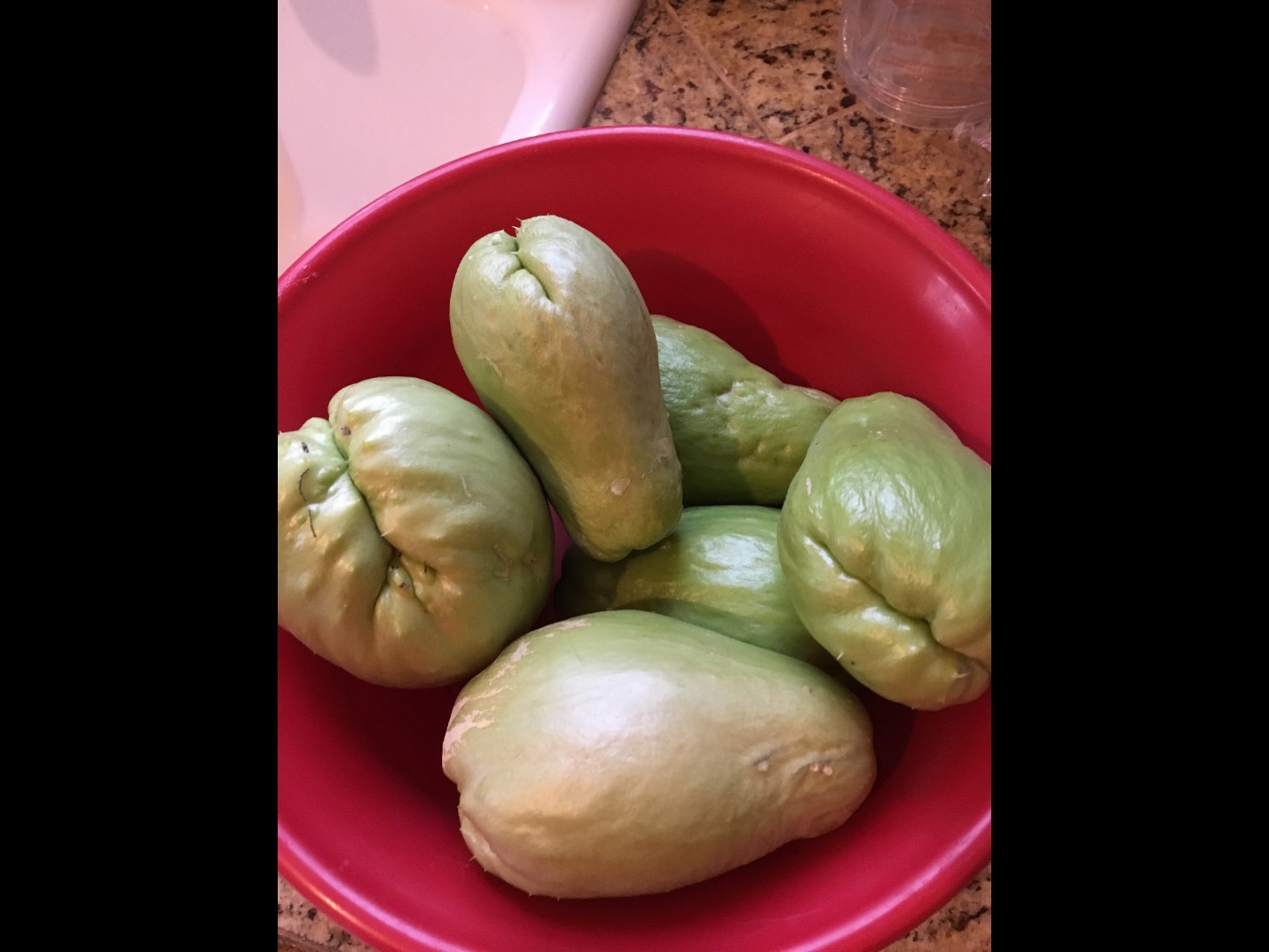
 Lapeyrolerie Mirlitons
Lapeyrolerie Mirlitons


 Lapeyrolerie Mirlitons
Lapeyrolerie Mirlitons




Recent Comments